IT Recruitment Overview
The global IT recruitment landscape has undergone dramatic transformations in recent years, with market dynamics shifting from the post-pandemic hiring surge to a more nuanced, competitive environment. As companies navigate the complexities of building high-performing technical teams, understanding both regional market conditions and proven best practices has become crucial for recruitment success.
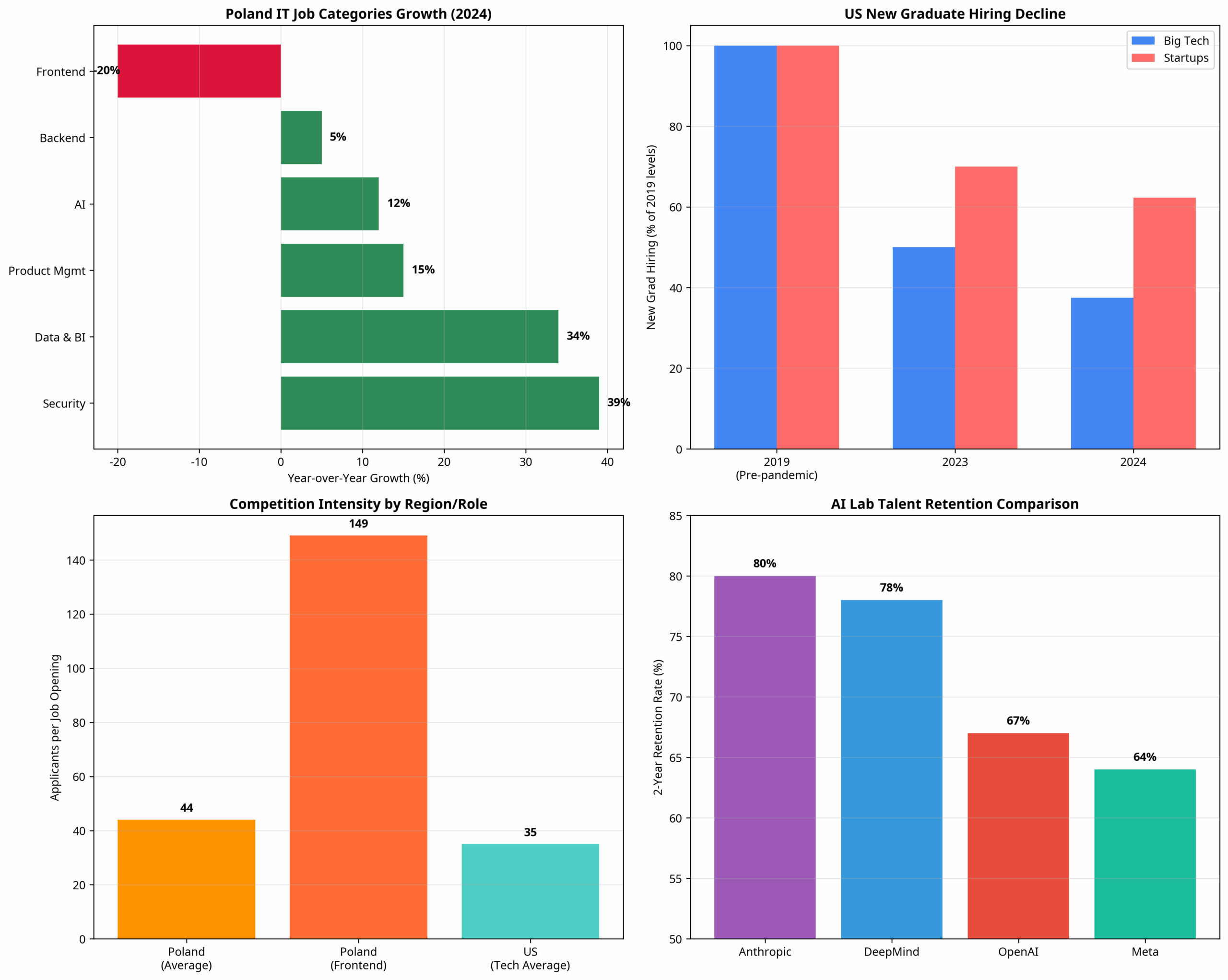
Recent data from Poland’s thriving IT sector reveals fascinating insights into European hiring trends, while Silicon Valley continues to set the pace for innovative recruitment strategies. In Poland, the IT job market showed signs of stabilization in 2024, with only 2.6% fewer job advertisements compared to the previous year, yet competition intensified significantly with an average of 44 people applying for each IT position—up from 40 in 2023 [1]. Meanwhile, across the Atlantic, the US tech industry faces its own challenges, with new graduate hiring plummeting by 50% compared to pre-pandemic levels, forcing companies to completely rethink their talent acquisition strategies [2].
IT Recruitment Global Trends
1. Embrace Speed-to-Hire as a Competitive Advantage
In today’s hyper-competitive talent market, velocity in hiring decisions can make the difference between securing top talent and losing candidates to competitors. Silicon Valley pioneers like Meta have revolutionized this approach through their “blitzscaling” methodology, prioritizing speed over perfection in candidate evaluation [3]. This strategy recognizes that in a market where the best candidates receive multiple offers, the company that moves fastest often wins.
The data supports this urgency-driven approach. Research from Poland’s IT market shows that the median time to hire for software engineers stands at 36 days [4], but companies that can reduce this timeline gain significant advantages. Meta’s approach involves making offers to promising candidates before they complete interviews elsewhere, sometimes extending offers within 24-48 hours of initial contact for exceptional talent [3].
However, speed must be balanced with quality assessment. The most successful implementations of rapid hiring involve pre-established evaluation frameworks that allow quick but thorough candidate assessment. Companies should develop standardized technical assessments that can be completed within 2-3 hours, coupled with behavioral interviews that focus on core competencies rather than exhaustive cultural fit evaluations.
The key is preparation. Organizations that excel at speed-to-hire maintain active talent pipelines, pre-approved compensation bands, and streamlined decision-making processes. They also invest in hiring manager training to ensure consistent, rapid evaluation criteria across all interviewers.
2. Leverage Data-Driven Compensation Strategies
Compensation remains the primary driver of talent acquisition and retention, but successful companies go beyond simply offering competitive salaries. They use sophisticated data analysis to understand market dynamics and create compelling total compensation packages that address candidate motivations beyond base pay.
Poland’s IT market provides valuable insights into compensation trends. While salary growth has moderated significantly—with increases typically limited to a few percentage points compared to the 15-20% annual increases seen in previous years—companies are finding success through creative compensation structuring [1]. The most effective approaches combine competitive base salaries with performance bonuses, equity participation, and comprehensive benefits packages.
In the US market, compensation strategies have become increasingly sophisticated. Leading AI companies like Anthropic have achieved remarkable 80% retention rates partly through compensation packages that extend beyond traditional salary structures [2]. These packages often include significant equity components, flexible work arrangements, and professional development budgets that can exceed $10,000 annually per employee.
The data reveals important regional differences. While Polish IT professionals increasingly value work-life balance and professional development opportunities, US tech workers often prioritize equity upside and cutting-edge project exposure. Successful recruitment strategies tailor compensation discussions to these regional preferences while maintaining competitive market positioning.
Companies should establish regular compensation benchmarking processes, utilizing multiple data sources including industry reports, peer company surveys, and real-time market intelligence. The most effective organizations update their compensation bands quarterly and empower hiring managers with real-time market data during salary negotiations.
3. Focus on High-Growth Technical Specializations
Market data clearly indicates which technical specializations are experiencing the strongest demand growth, and successful recruitment strategies align with these trends. Poland’s IT market demonstrates this principle effectively, with Security roles showing a remarkable 39% year-over-year increase in job postings, while Data & Business Intelligence positions grew by 34% [1]. These growth areas represent opportunities for companies to build competitive advantages through early talent acquisition.
The shift away from traditional programming roles is particularly noteworthy. While Backend development still represents the largest category of job postings at 20% of the market, the combined share of strictly programming specializations has declined to just 36.6% of total IT advertisements—down from over 50% just two years ago [1]. This trend reflects the industry’s evolution toward more specialized, high-value technical roles that require deep domain expertise.
In the US market, similar patterns emerge with even more pronounced specialization. AI and machine learning roles are projected to grow by 17% annually, while traditional software development positions face increased competition from automation tools [5]. Companies like Anthropic have capitalized on this trend by focusing recruitment efforts on specialized AI researchers and engineers, achieving superior retention rates through targeted hiring in high-growth areas [2].
The strategic implication is clear: organizations should prioritize recruitment in emerging technical specializations while maintaining core development capabilities. This approach requires proactive talent pipeline development, often involving partnerships with universities, specialized training programs, and targeted recruitment from companies working in adjacent technologies.
Successful implementation involves creating specialized career tracks for high-growth areas, offering premium compensation for scarce skills, and developing internal training programs that can upskill existing team members into emerging specializations. Companies should also consider geographic arbitrage, leveraging Poland’s strong technical education system and competitive costs for specialized roles that can be performed remotely.
4. Implement Rigorous Cultural Integration Processes
While technical skills remain paramount, cultural integration has emerged as a critical factor in long-term hiring success. The most successful Silicon Valley companies have moved beyond simple “cultural fit” assessments to develop sophisticated cultural integration processes that help new hires thrive in high-performance environments.
Meta’s approach exemplifies this evolution. Rather than focusing on whether candidates fit existing culture, they prioritize raw talent and invest heavily in cultural integration during onboarding [3]. This strategy recognizes that exceptional technical talent can adapt to organizational culture when provided with proper support and clear expectations.
The data supports this approach. Companies with structured cultural integration programs report 25% higher retention rates and 40% faster time-to-productivity for new hires [6]. These programs typically include mentorship assignments, structured feedback cycles, and clear performance expectations that help new team members understand both technical requirements and cultural norms.
Anthropic’s remarkable 80% retention rate partly stems from their unique cultural approach that embraces intellectual discourse and researcher autonomy [2]. Their integration process focuses on giving new hires immediate access to meaningful projects while providing the support structure necessary for success in a fast-paced research environment.
Effective cultural integration requires systematic approaches. Companies should develop standardized onboarding curricula that extend beyond technical training to include company values, communication norms, and decision-making processes. The most successful programs pair new hires with experienced mentors and establish regular check-in processes during the first 90 days of employment.
The key insight is that cultural integration is a learnable skill, not an innate characteristic. Organizations that invest in systematic cultural integration processes can successfully hire exceptional talent from diverse backgrounds while maintaining strong team cohesion and performance standards.
5. Develop Global Talent Sourcing Capabilities
The most successful tech companies have abandoned geographic limitations in favor of global talent sourcing strategies that access the best candidates regardless of location. This approach has become particularly important as remote work capabilities have matured and companies compete for increasingly scarce specialized skills.
Silicon Valley companies lead this trend through sophisticated global hiring programs. Meta, Google, and other tech giants maintain recruitment operations across multiple continents, often establishing regional hubs that provide access to local talent markets while maintaining connection to core operations [3]. This strategy allows companies to access diverse skill sets while managing costs through geographic arbitrage.
Poland represents an excellent example of successful global talent sourcing. The country’s ICT market is projected to reach $31.6 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 10.1% through 2030 [7]. Polish developers consistently rank among the top performers in international programming competitions, with the country placing third globally in technical skills assessments and ranking sixth on TopCoder for first-place finishes [8].
The strategic advantages of global sourcing extend beyond cost considerations. Different regions offer distinct technical strengths—Poland excels in backend development and cybersecurity, India provides strong capabilities in data science and AI, while Eastern European countries offer exceptional mobile development expertise. Companies that understand these regional strengths can build more capable teams through targeted geographic recruitment.
Successful global sourcing requires sophisticated operational capabilities. Companies must develop expertise in international employment law, establish effective remote collaboration processes, and create compensation frameworks that account for regional market differences while maintaining internal equity. The most successful implementations involve establishing regional recruitment hubs with local expertise and cultural understanding.
Technology infrastructure plays a crucial role in global talent sourcing success. Companies need robust communication platforms, collaborative development environments, and project management systems that enable seamless integration of distributed teams. Investment in these capabilities often pays dividends through access to broader talent pools and improved team diversity.
6. Prioritize Retention Through Career Development
With competition for IT talent intensifying globally, retention has become as important as initial recruitment. The most successful companies recognize that career development opportunities often outweigh compensation considerations in long-term retention decisions, particularly for high-performing technical professionals.
The data reveals significant retention challenges across the industry. In Poland’s competitive market, companies face increasing pressure as talented professionals receive multiple offers and career advancement opportunities [1]. Similarly, US tech companies struggle with retention as AI labs and startups aggressively recruit experienced professionals with compelling career growth propositions [2].
Anthropic’s exceptional 80% retention rate provides valuable insights into effective retention strategies. Their approach emphasizes intellectual autonomy, meaningful project assignments, and clear paths for technical advancement without forced management transitions [2]. This model recognizes that many technical professionals prefer deep specialization over traditional management career tracks.
Successful retention strategies require systematic career development programs that provide multiple advancement pathways. Companies should establish technical leadership tracks that allow senior engineers to advance without becoming people managers, create rotation programs that expose high-potential employees to different technical domains, and provide substantial professional development budgets that enable continuous skill enhancement.
The most effective programs combine formal training opportunities with practical project assignments that stretch employee capabilities. Companies like DeepMind and Google maintain internal research programs that allow employees to pursue cutting-edge technical projects while contributing to business objectives [2]. These programs serve dual purposes of advancing company capabilities while providing compelling career development opportunities for top talent.
Mentorship programs represent another crucial retention tool. Pairing experienced professionals with high-potential employees creates knowledge transfer opportunities while building stronger organizational connections. The most successful mentorship programs include structured goals, regular feedback mechanisms, and clear success metrics that benefit both mentors and mentees.
Regular career planning conversations are essential for retention success. Companies should establish quarterly career development discussions that go beyond performance reviews to explore employee aspirations, identify skill gaps, and create concrete development plans. These conversations help employees see long-term growth opportunities within the organization while providing managers with insights into retention risks.

Align Team Culture
correct context it recruitment
7. Leverage Technology for Efficient Candidate Assessment
Modern recruitment success increasingly depends on sophisticated technology platforms that can efficiently evaluate technical capabilities while providing positive candidate experiences. The most successful companies have moved beyond traditional resume screening to implement comprehensive assessment technologies that provide deeper insights into candidate potential.
The scale of modern recruitment challenges demands technological solutions. With Poland’s IT market seeing 44 applicants per position on average, and Frontend roles attracting 149 candidates each [1], manual screening processes become impractical for high-volume recruitment. Companies need automated systems that can quickly identify the most promising candidates while maintaining assessment quality.
Silicon Valley companies lead in recruitment technology adoption. Many organizations now use AI-powered screening tools that analyze coding samples, assess problem-solving approaches, and evaluate communication skills through structured exercises [3]. These tools enable rapid candidate evaluation while providing consistent assessment criteria across all applicants.
However, technology must enhance rather than replace human judgment. The most effective implementations combine automated screening with human evaluation for final candidate selection. This hybrid approach allows companies to process large candidate volumes efficiently while ensuring that final hiring decisions incorporate nuanced assessments of cultural fit and growth potential.
Successful technology implementation requires careful platform selection and ongoing optimization. Companies should choose assessment tools that align with their specific technical requirements, provide positive candidate experiences, and generate actionable insights for hiring decisions. Regular calibration of assessment criteria ensures that technology platforms continue to identify candidates who succeed in actual job performance.
The candidate experience aspect of recruitment technology cannot be overlooked. Assessment platforms should provide clear instructions, reasonable time requirements, and meaningful feedback to candidates regardless of hiring outcomes. Companies that prioritize positive candidate experiences through technology often see improved employer brand perception and higher acceptance rates for extended offers.
8. Build Strategic Talent Pipelines
Proactive talent pipeline development has become essential for companies operating in competitive IT markets. Rather than reactive hiring in response to immediate needs, the most successful organizations maintain ongoing relationships with potential candidates and build talent communities that can be activated when opportunities arise.
The urgency of pipeline development is evident in current market conditions. With US new graduate hiring down 50% from pre-pandemic levels and experienced professionals receiving multiple offers [2], companies cannot rely on traditional job posting strategies. They need systematic approaches to talent relationship building that create competitive advantages when hiring needs emerge.
Leading companies implement multi-channel pipeline strategies that include university partnerships, professional community engagement, and alumni networks. Meta and other Silicon Valley companies maintain active relationships with computer science programs at top universities, providing internship opportunities, guest lectures, and research collaborations that create early connections with emerging talent [3].
Professional community engagement represents another crucial pipeline development strategy. Companies should participate in technical conferences, sponsor open-source projects, and contribute to professional development initiatives that build brand recognition among target talent communities. These activities create positive associations that influence candidate decisions when opportunities arise.
Alumni networks provide particularly valuable pipeline opportunities. Former employees often become excellent sources of referrals and may return to organizations where they had positive experiences. Companies should maintain active alumni communities through regular communication, professional development opportunities, and clear pathways for re-engagement.
The most effective pipeline strategies involve systematic relationship management. Companies should use customer relationship management (CRM) systems adapted for talent acquisition, maintaining detailed records of candidate interactions, skill assessments, and career progression. This approach enables personalized outreach when relevant opportunities become available.
Content marketing has emerged as a powerful pipeline development tool. Companies that regularly publish technical content, share engineering insights, and demonstrate thought leadership attract passive candidates who may not actively seek new opportunities but remain open to compelling propositions. This approach builds long-term brand recognition that influences candidate decisions when they do enter the job market.
9. Implement Flexible Work Arrangements Strategically
The evolution of work arrangements has fundamentally changed recruitment dynamics, with flexibility becoming a key differentiator in talent acquisition. However, successful implementation requires strategic thinking about which roles benefit from flexibility and how to maintain team cohesion in distributed environments.
Market data demonstrates the importance of work arrangement flexibility. Poland’s IT market shows that hybrid work models dominate among IT professionals, with only a small percentage working entirely on-site [9]. This trend reflects broader industry shifts toward flexible arrangements that accommodate diverse employee preferences while maintaining operational effectiveness.
Silicon Valley companies have pioneered sophisticated approaches to flexible work arrangements. Rather than blanket remote work policies, leading organizations develop role-specific flexibility frameworks that consider collaboration requirements, security constraints, and performance measurement capabilities [3]. This nuanced approach allows companies to offer compelling flexibility while maintaining operational excellence.
The key insight is that flexibility must be purposeful rather than universal. Roles requiring intensive collaboration, such as product development and research, may benefit from hybrid arrangements that combine remote work with regular in-person collaboration. Conversely, individual contributor roles in areas like backend development or data analysis may function effectively in fully remote environments.
Successful flexible work implementation requires investment in collaboration infrastructure. Companies need robust communication platforms, project management systems, and virtual collaboration tools that enable effective teamwork across distributed teams. The most successful implementations also establish clear communication protocols and performance expectations that work across different work arrangements.
Cultural considerations play a crucial role in flexible work success. Organizations must develop management practices that focus on outcomes rather than activity monitoring, create inclusive meeting practices that engage both remote and in-person participants, and maintain team building activities that build relationships across distributed teams.
The recruitment advantage of strategic flexibility is significant. Companies that offer thoughtful, role-appropriate flexible arrangements often attract candidates who might otherwise be unavailable due to geographic constraints or personal circumstances. This expanded talent pool can provide access to exceptional candidates who prioritize work-life integration alongside career advancement.
10. Create Compelling Employer Brand Narratives
In an increasingly competitive talent market, employer brand differentiation has become crucial for recruitment success. The most successful companies develop compelling narratives that communicate their unique value propositions and attract candidates who align with their mission and culture.
The importance of employer branding is evident in retention data. Anthropic’s exceptional 80% retention rate partly stems from their distinctive brand narrative that emphasizes intellectual discourse, researcher autonomy, and meaningful AI safety work [2]. This clear positioning attracts candidates who value these characteristics and are more likely to remain engaged long-term.
Effective employer branding goes beyond traditional benefits and compensation messaging. Companies should articulate their technical vision, demonstrate their commitment to professional development, and showcase the impact that employees can achieve through their work. The most compelling narratives combine mission-driven messaging with concrete examples of employee growth and achievement.
Content strategy plays a crucial role in employer brand development. Companies should regularly publish technical content that demonstrates their engineering capabilities, share employee success stories that illustrate career development opportunities, and provide insights into their technical decision-making processes. This content builds credibility while attracting candidates who appreciate the company’s technical approach.
Social proof represents another powerful employer branding tool. Employee testimonials, technical conference presentations, and industry recognition provide third-party validation of company claims about culture and technical excellence. Companies should systematically collect and share these endorsements across their recruitment marketing channels.
The most successful employer brands are authentic and consistent across all touchpoints. From initial candidate outreach through onboarding and ongoing employment, companies should deliver experiences that align with their brand promises. Inconsistency between brand messaging and actual employee experience undermines recruitment effectiveness and increases turnover risk.
Measurement and optimization are essential for employer brand success. Companies should track brand perception metrics, monitor candidate feedback, and analyze recruitment funnel performance to identify improvement opportunities. Regular brand audits help ensure that messaging remains relevant and compelling as company culture and market conditions evolve.
Conclusion
The IT recruitment landscape continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancement, changing work preferences, and intensifying competition for specialized talent. Success in this environment requires sophisticated strategies that combine data-driven decision making with human-centered approaches to talent acquisition and retention.
The contrast between Poland’s stabilizing market and the US’s dramatic shifts in hiring patterns illustrates the importance of regional market understanding. While Polish companies navigate intense competition with 44 applicants per position, US organizations grapple with talent scarcity in senior roles and oversupply in junior positions. These different dynamics require tailored approaches that account for local market conditions while incorporating global best practices.
The ten strategies outlined in this analysis provide a comprehensive framework for recruitment success across different market conditions. From speed-to-hire advantages and data-driven compensation to global talent sourcing and compelling employer branding, these approaches address the full spectrum of modern recruitment challenges.
Perhaps most importantly, successful IT recruitment requires long-term thinking that extends beyond immediate hiring needs. Companies that invest in talent pipeline development, systematic retention strategies, and authentic employer brand building create sustainable competitive advantages that compound over time. In a market where the best talent has multiple options, these investments in relationship building and organizational excellence often determine recruitment success.
As the industry continues to evolve, companies that remain adaptable while maintaining focus on fundamental recruitment principles will be best positioned to build exceptional technical teams. The data clearly shows that recruitment success increasingly depends on sophisticated strategies that combine technological capabilities with deep understanding of candidate motivations and market dynamics.
References
[1] No Fluff Jobs. (2024). IT Job Market in Poland in 2024 report. Retrieved from https://nofluffjobs.com/en/insights/report-it-job-market-in-poland-2024/
[2] SignalFire. (2025). The SignalFire State of Tech Talent Report – 2025. Retrieved from https://www.signalfire.com/blog/signalfire-state-of-talent-report-2025
[3] Talcom. (2025). Blitzscaling Talent: How Silicon Valley hire top tech talent in a hyper-competitive market. Retrieved from https://www.talcom.nl/blog/blitzscaling-talent
[4] Agency Partners. (2025). Hire GoLang Developers in Wrocław – Market trends and insights. Retrieved from https://agency-partners.com/reports/market-insights/poland-wrocaw-software-go
[5] Course Report. (2025). Where are all America’s tech workers in 2025? Retrieved from https://www.coursereport.com/reports/techxodus
[6] Toggl Hire. (2025). 12 Recruitment Best Practices for 2025. Retrieved from https://toggl.com/blog/recruitment-best-practices
[7] Simply Talented. (2025). The Polish IT Job Market: Our Observations on Standing Out in a Select Pool. Retrieved from https://wearesimplytalented.com/the-polish-it-job-market-our-observations-on-standing-out-in-a-select-pool/
[8] Alcor BPO. (2025). Software Development in Poland in 2025. Retrieved from https://alcor-bpo.com/software-development-in-poland-facts-and-new-reality/
[9] Statista. (2024). IT professionals working model in Poland 2024. Retrieved from https://www.statista.com/statistics/1609718/poland-it-professionals-working-model/


